In the 1800s, more than 46% of children died before turning five, mostly due to infectious diseases. But by 2020, child mortality dropped to just seven deaths per 1,000 births, marking a historic low. This remarkable progress is largely thanks to advancements in healthcare, sanitation, and vaccines.
Vaccines have proven to be one of the most effective tools in saving young lives. They have prevented an estimated 154 million deaths worldwide, including 146 million children under the age of five. Of these, 101 million were infants under one year old. Vaccination has not only spared countless families from devastating loss but also revolutionized global health.
However, this progress is under threat. Vaccine hesitancy and mistrust are on the rise, leading to a resurgence of diseases like polio and measles, once eradicated.

According to the World Health Organization (WHO), since September of this year, poliovirus has been detected in five countries in the European Region (Finland, Germany, Poland, Spain, and the United Kingdom) through routine wastewater system surveillance. The WHO states that even though no cases have been found to date, the presence of virus highlights the value of vaccination and surveillance, as well as the continuous threat that any type of poliovirus poses to all nations worldwide.
As Per the WHO, Polio (poliomyelitis) mainly affects children under 5 years of age. One in 200 infections leads to irreversible paralysis. Among those paralysed, 5–10% die when their breathing muscles become immobilized. Cases due to wild poliovirus have decreased by over 99% since 1988, from an estimated 350 000 cases in more than 125 endemic countries, to just two endemic countries.
- As long as a single child remains infected, children in all countries are at risk of contracting polio. Failure to eradicate polio from these last remaining strongholds could result in a global resurgence of the disease.
As per a video news report published by Voice of America reported that polio remains active in only two countries in the world: Pakistan and Afghanistan. Over 50 cases of so-called wild polio have been confirmed in the region this year despite continuing efforts to eradicate the disease.
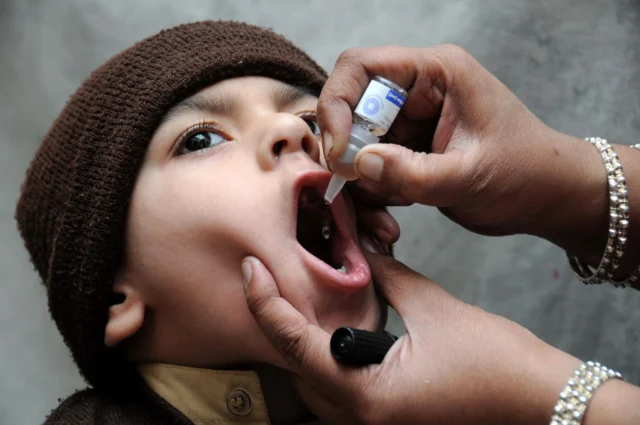
Importance of vaccination in kids and mother

According to Dr. Ashish Tiwari, Director of ACS Health, Mumbai, vaccination is vital for protecting children and mothers from debilitating diseases like polio. It not only ensures individual health but also contributes to community health through herd immunity, reduces the chances of disease outbreaks, and supports global health efforts. By vaccinating children and ensuring that mothers are up to date with their immunizations, we can prevent the spread of diseases, reduce suffering, and create healthier, more resilient communities.
The Impact of Low Vaccination Rates
Dr. Tiwari warns that low vaccination rates pose significant risks to public health, including increased disease outbreaks, higher mortality and morbidity, and strain on healthcare systems. It weakens herd immunity, putting vulnerable populations at greater risk, and can have widespread economic and global consequences.
Primary reasons behind vaccine hesitancy and mistrust
Dr. Tiwari claims that there are several factors contributing to vaccine hesitancy, including misinformation, disinformation, distrust in healthcare systems, fear of side effects, cultural and religious beliefs, and complacency.
Strategies to increase vaccination coverage and address hesitancy
Dr. Tiwari said, to address these issues, governments and organizations requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes providing clear and accurate information to counter misinformation, building trust in healthcare systems, ensuring vaccines are accessible and affordable, and engaging with communities to understand and respect their concerns. He added that partnerships with local leaders, transparent communication, and the use of incentives or mandates can further encourage vaccination.
lessons we can learn from countries with high vaccination rates
Dr. Tiwari highlights that countries with high vaccination rates offer valuable lessons for improving global immunization efforts. These include the importance of strong healthcare infrastructure, effective public education campaigns, universal access to vaccines, community engagement and trust-building are key. He stresses the importance of sustained vaccination efforts and emphasizes that collaboration between governments, international organizations, and local communities ensures that vaccines reach everyone.
Global cooperation is essential
Dr. Tiwari emphasizes that global cooperation is essential in eradicating poliovirus and similar health threats because diseases do not recognize borders. Collaborative efforts ensure universal vaccination, resource sharing, and effective surveillance, which are crucial for controlling and eliminating these diseases. By uniting, countries can address challenges in hard-to-reach areas, maintain sustained immunization campaigns, and share knowledge and expertise.




