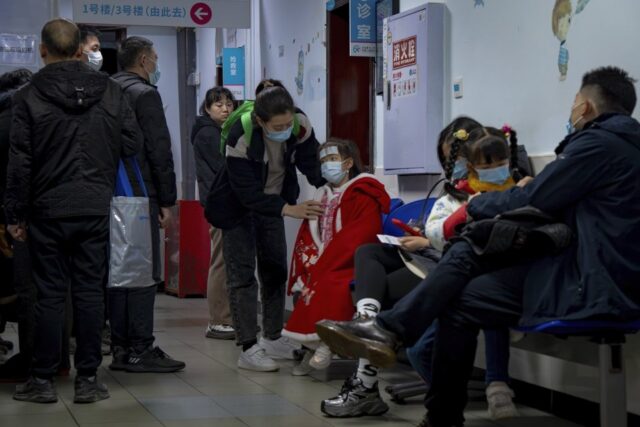
The rate of infections with the flu-like human metapneumovirus (HMPV) virus in northern China is declining, a health official said on Sunday, addressing international concerns about a potential pandemic.
HMPV, which belongs to the same family as the respiratory syncytial virus, causes flu or cold-like symptoms including fever, cough and nasal congestion. While symptoms often resolve on their own, the virus can cause lower respiratory tract infections among children, elderly and those immunocompromised.
Wang Liping, a researcher at the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, explained during a briefing by China’s National Health Commission that HMPV is not a new virus and has been present for decades. Detected in the Netherlands in 2001, its recent rise in reported cases is due to better detection methods.
“Currently, the rate of positive HMPV cases in northern provinces is declining, particularly among patients aged 14 and below,” she said.
Concerns surfaced in recent days over a surge in HMPV infections in northern China after images circulated online of hospitals overrun with masked patients. However, the World Health Organization clarified it has not received any reports of unusual outbreaks in China or anywhere else.
Experts emphasize that HMPV differs significantly from COVID-19, as most children are infected by the age of five, providing some level of built-in immunity.
Wang reassured the public that respiratory illnesses in China are caused by known pathogens, with no new infectious diseases detected.
Currently, there are no vaccines or drug available for HMPV. To prevent infection, health authorities recommend frequent handwashing, avoiding crowded places when possible, and wearing masks in public spaces.