Human milk (HM) is an essential source of nutrition for preterm infants, offering a unique composition of bioactive compounds, immunological factors, and macronutrients crucial for growth and development. In preterm neonates, HM not only supports nutrition but also reduces the risk of severe morbidities such as necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), bronchopulmonary dysplasia, and late-onset sepsis. However, several maternal and perinatal factors may influence both the volume and composition of HM.
This prospective longitudinal study evaluates HM production and macronutrient composition during the first 15 days of life in mothers of premature infants. Key variables examined include maternal age, type of delivery, and newborn sex, focusing on their effects on early lactation performance and nutritional quality of milk.
Study Design and Methodology
This 2-year longitudinal prospective study conducted at the University Clinical Hospital of Santiago de Compostela, a Level III Q3+ facility. A total of 45 mothers of 52 preterm infants (gestational age ≤32 weeks and/or birth weight ≤1500 g) were included.
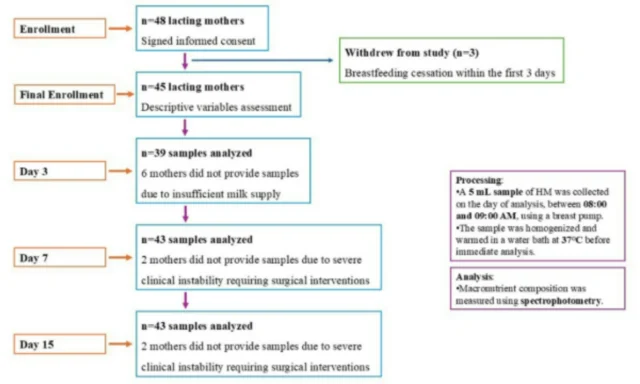
The study spanned the first 15 days of neonatal life. Daily milk expression volumes were recorded, and milk samples were collected on days 3, 7, and 15 for macronutrient analysis. Macronutrient profiling (proteins, fats, and carbohydrates) was performed using Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy via the MilkoScan Mars analyzer (FOSS Denmark), following standardized sample preparation procedures including warming, homogenization, and immediate testing.
Data analysis was conducted IBM SPSS Statistics version 20.0 software. Given the non-parametric distribution of most variables (verified using the Shapiro–Wilk test), the Mann–Whitney U test was employed for comparisons of continuous variables, and chi-square tests for categorical data. Statistical significance was defined as p ≤ 0.05.
Results and Key Findings
- Milk Volume Trends and Predictors of Lactation Success
A critical finding of the study was the predictive value of HM volume expressed on day 4. Mothers producing less than 140 mL/day on this day had a significantly higher likelihood (p = 0.003) of failing to reach 500 mL/day by day 15—a threshold associated with successful exclusive breastfeeding at hospital discharge in other studies. Notably, 64.3% of mothers in the sample fell below the 140 mL/day mark on day 4, and 73.8% of these did not achieve 500 mL/day by day 15.
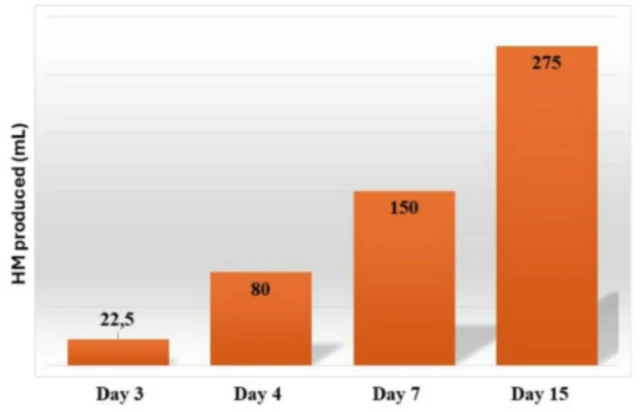
This emphasizes the importance of early milk volume monitoring in NICUs. Early intervention, including lactation counselling and frequent milk expression, can potentially alter this trajectory and improve lactation outcomes.
- Impact of Mode of Delivery
While statistical comparisons of HM volumes on days 3, 7, and 15 showed no significant differences between vaginal and cesarean deliveries, a trend toward higher milk production following vaginal delivery was evident on days 7 and 15. Cesarean deliveries, often associated with delayed onset of lactogenesis II, may contribute to this observed disparity, potentially due to the influence of anesthesia, maternal-infant separation, and stress responses.
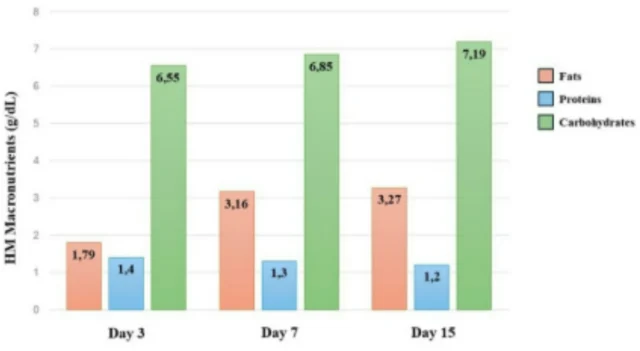
Moreover, a statistically significant difference in fat content was observed on day 3 (p = 0.03), with colostrum from vaginal births exhibiting higher fat levels. This early divergence in macronutrient composition highlights the physiological advantage of spontaneous labor in initiating robust lactogenesis.
- Influence of Maternal Age
Although no statistically significant differences were detected in HM volumes or macronutrient composition based on maternal age, a consistent trend was observed wherein mothers aged ≥35 years produced less milk compared to their younger counterparts across all time points. Advanced maternal age may be associated with hormonal variations or comorbidities that impact milk production, although further research is needed to clarify these mechanisms. - Infant Sex and Milk Composition
Contrary to some previous findings suggesting sex-based variations in HM composition, particularly in carbohydrate content, this study found no significant differences in macronutrient profiles based on the sex of the infant at any point. While trends may exist, the small sample size could have limited the power to detect subtle differences. - Overall Macronutrient Trends
Across the 15-day period, protein content remained relatively stable, while fat and carbohydrate levels increased progressively. This aligns with known lactation physiology, where colostrum transitions to mature milk, adapting to the nutritional needs of the developing infant.
Discussion
The findings of this study underscore the dynamic nature of HM in the context of prematurity and the significance of early lactation management. Initiation of colostrum expression within the first hour after birth and promoting frequent expression near the infant or during Kangaroo Mother Care can enhance milk output and expedite the onset of lactogenesis II.
Given the high predictive value of milk volume on day 4, incorporating early lactation assessments into standard NICU practice may enable timely interventions. Mothers with low early output can benefit from additional support, including skin-to-skin contact, psychological counseling, and structured expression schedules.
The observed influence of delivery mode on fat content and volume also calls for targeted postpartum lactation strategies for mothers undergoing cesarean sections. Lactation consultants and NICU nurses should pay special attention to these mothers, helping mitigate delays in lactogenesis and supporting sustained milk production.
Despite the absence of strong statistical associations between maternal age and HM parameters, trends suggest that older mothers might face additional challenges in establishing robust milk supply, warranting further investigation with larger cohorts.
Conclusion
Human milk production in mothers of preterm infants is a complex, multifactorial process influenced by maternal and perinatal variables. The volume of HM expressed on day 4 postpartum is a strong predictor of future lactation success. Vaginal delivery and maternal age below 35 years are associated with more favorable HM production outcomes, while cesarean sections may impair both volume and early fat content. No significant influence of infant sex was observed on HM composition.
Importantly, macronutrient composition evolves significantly during the initial postpartum period, reflecting the adaptive capacity of HM to meet the developmental needs of preterm infants. This study reinforces the need for proactive lactation support strategies tailored to individual maternal profiles, ultimately promoting exclusive HM feeding and improved neonatal health outcomes.