The number of women undergoing breast cancer treatment in India is projected to rise by 50,000 annually throughout this decade, with the economic burden expected to average $19.55 billion per year, according to a new study published in Nature with the title “Economic Burden of Breast Cancer in India, 2000–2021 and Forecast to 2030”.
The research analyses data from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) database to estimate annual prevalence and applies a statistical model (ARIMA) to forecast future trends, adjusting for past patterns and fluctuations.
The study employs a bottom-up approach to calculate the direct costs of breast cancer, including hospital visits, treatment, and follow-up care. It draws on a study by the International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS) in Mumbai, which tracked 500 breast cancer patients over 34 months at the Tata Memorial Centre. Findings reveal that the majority of breast cancer patients in India face catastrophic health expenditures, with rural, poor, and agricultural households bearing the heaviest financial burden.
“We haven’t accounted for the depreciating currency value or the costs at private healthcare facilities. The study is based on treatment costs till 2021 due to limited data, meaning the economic burden we’ve cited is an underestimation,” said Dr. Denny John, Professor of Public Health at M.S. Ramaiah University of Applied Sciences, who supervised the study’s methodology.
The research does not account for the varying costs of different stages of breast cancer treatment. For example, Kashaf Shaikh (34), diagnosed with triple-negative breast cancer in 2019, spent Rs 18 lakh on diagnosis, chemotherapy, radiation, surgery, and other treatments at private hospitals, expenses she could only afford with family support.
What is breast cancer and its stages?
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers that affects women. It happens when cancerous cells in your breasts multiply and become tumors. Breast cancer typically affects women aged 50 and older. There are five stages of breast cancer: 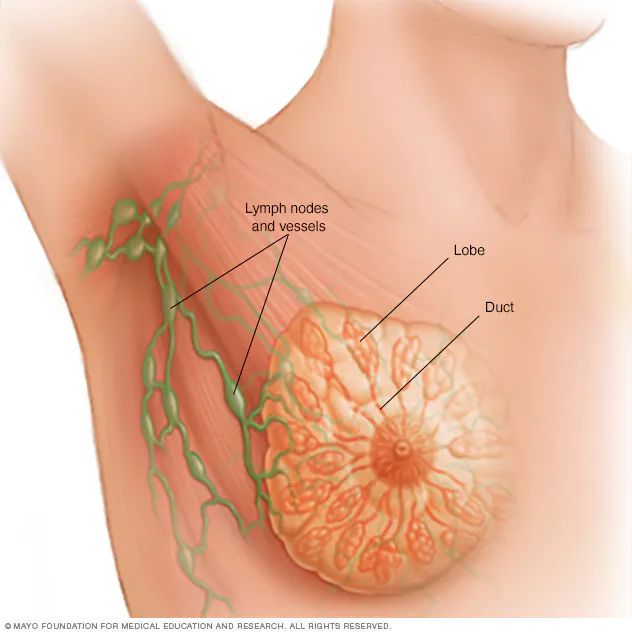
Stage 0: Non-invasive breast cancer in milk duct.
Stage I: There are cancerous cells in nearby breast tissue.
Stage II: The cancer is in the breast and nearby lymph nodes
Stage III: There’s breast cancer in nearby tissue and lymph nodes. Stage III is usually referred to as locally advanced breast cancer.
Stage IV: The cancer has spread to other organs in the body, such as the bones, lungs, brain, liver, or distant lymph nodes
Dr. Vani Parmar, Chief of Breast Surgical Oncology at Punyashlok Ahilyadevi Holkar Head and Neck Cancer Institute (formerly at Tata Memorial Hospital), explained that treatment costs are multifaceted and significantly impact daily incomes, especially for younger working women. “While medical advances improve outcomes, they come with high costs. Financial assistance is available at Tata Memorial Hospital, where drugs are heavily subsidized, and discounts are offered. Unfortunately, not all private hospitals can afford to offer such subsidies.”
Non-Communicable Diseases: A Growing Health Concern in Urban India
Dr. John emphasized that the study aims to raise awareness about the economic impact of breast cancer on India’s GDP, urging policymakers to invest in health infrastructure. “Women are a significant part of our workforce. This is a warning for Indian companies to implement more supportive policies for their employees,” he said.




